By Jane Barthelemy.
By Jane Barthelemy.
Many people ask me why they tend to come down with colds and flu. In a group of people where someone is sick, they’re always the first person to catch a bug. Our common understanding of the immune system is based on bit of everything – traditional beliefs, our doctor’s medical advice, our parents, the media, pharmaceutical ads, personal experience, etc. This article explores both Western and Chinese medicine on the immune system. Recently a totally new world of discovery has opened the scientific community, changing overnight our view of our immune system in enormous and colorful detail. This new knowledge holds great promise for better understanding of human health. It also offers opportunities for mass initiatives through manipulation of DNA and stem cells previously unanticipated, which could change the face of humanity.
Simply, How Can We Protect our Health and Build the Immune System?
Well, the Top 10 healthy lifestyle habits still apply:
- Drink plenty of pure water, 70 to 75 oz. per day. Enjoy green tea.
- Skip acidic foods like sugars, wheat, fruit juices, processed & refined foods, sweet fruits, cold foods and drinks, dairy, and deep fried foods.
- Eat an alkaline diet, fresh seasonal nutrient-dense foods, veggies lightly cooked, 3 small meals a day.
- Stay active. Move your body every day.
- Get 8 to 9 hours sleep every night.
- Avoid antibiotics, pharmaceuticals, GMO foods, chemical toxins, and vaccines.
- Walk outside in the sun 20 minutes every day, preferably in Nature.
- Meditation clears toxins and resets all body functions.
- Practice Qigong to build a strong Wei Qi protection.
- Use a daily nasal rinse such as NeilMed Sinus Rinse
Other Points:
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Get up with the sun. Go to bed early.
- Avoid emotional stress. Stop worrying. Turn off electronics at 8pm.
- Be kind to yourself. Practice self-love. Negative emotions increase risk of disease.
- Keep these herbs handy: Reishi Mushroom extract, John’s Wort, a bottle of Yu Ping Feng Wan, called the Jade Windscreen Formula.
- Enjoy sexual vitality, within reasonable bounds.
- Stay warm. Avoid getting chilled in the cold seasons.
Introduction to the Immune System
The Immune System is a vast network of cells and tissues that functions as a harmonious system, located throughout the body in the organs such as the lungs and heart. Its purpose is to protect us from the invasion of the wrong microbes. There are literally thousands of varieties of specialized seek-and-destroy blood cells in the body that protect us from “bad” microbes, good microbes out of place, and abnormal growths. The immune system is adaptable and intelligent. For example, it can learn about new pathogens and protect us against the latest mutation of a flu-virus. In addition, countless beneficial bacteria help to protect the body from pathogens and disease.
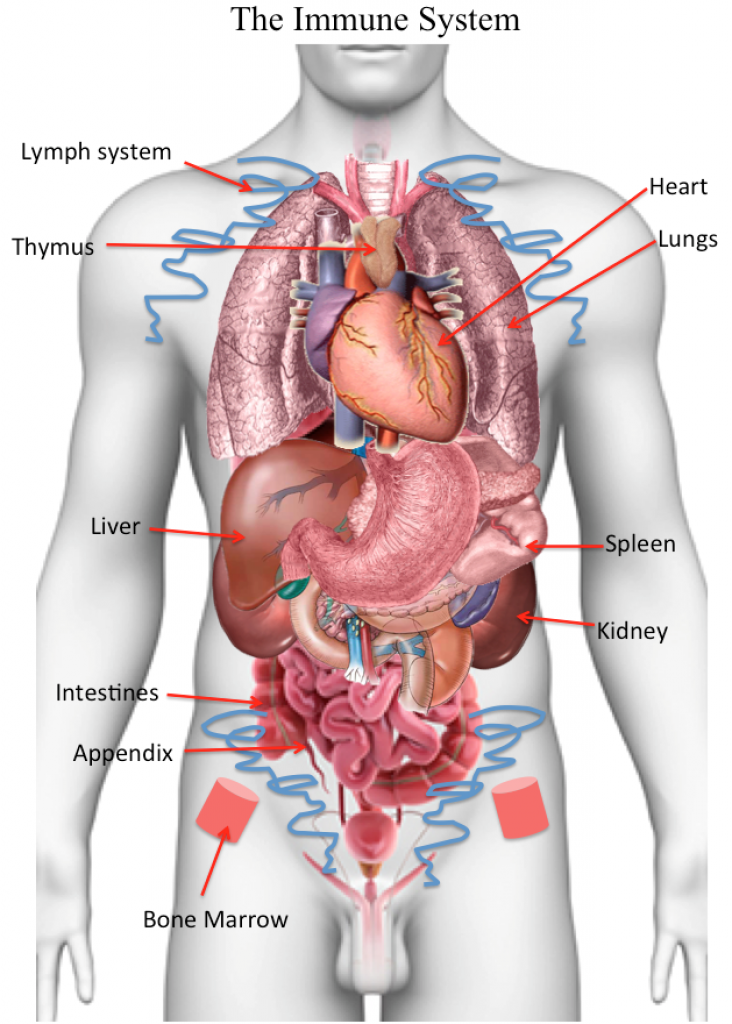
The Three Main Components of the Immune system are:
- Organs or Systems, such as the Lymph, Spleen, and Bone Marrow
- Protective Cells such as White Blood cells
- Beneficial Microbes, specialized in various roles
Organs of the Immune System
The organs of the immune system are the Heart, Lungs, Spleen, Liver, Thymus, Lymph system, Bone Marrow, Appendix, Intestines, especially Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT).
Heart – The heart regulates the immune activities.
The heart controls and regulates the flow of blood through the vessels of the body. In addition to pumping blood, Chinese Medicine views the heart as regulating the nervous, cardiovascular and endocrine functions, because, the heart houses the spirit (shen). When the heart’s “ruling” is good, then the other organ systems work in harmony, and the body can fight against diseases effectively.
Lungs – The lungs are an immuno-barrier.
The Lungs are a major detox organ in the body, through the air that we exhale. In Chinese medicine, the Lungs rule the Qi, or vital energy. They connect externally with the skin and hair to disseminate protective Qi over the body’s surface. This forms the first barrier against the invasion of exogenous pathogens.
Bone Marrow – All specialized immune cells come from stem cells in the bone marrow. New research reveals that the bone marrow produces stem cells, blood cells, and all immune system cells. All T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, natural killer T (NKT) cells, neutrophils, myeloid-derived suppressor cells and mesenchymal stem cells, come from the bone marrow. Bone marrow is now seen as an immune regulatory organ capable of fine tuning immunity and may be a potential therapeutic target for immunotherapy.
Thymus – T-cells mature in the Thymus.
Immature T-cells known as pre-T cells (or prothymocytes), leave the bone marrow and migrate into the thymus. The mature T cells are then released into the bloodstream. The Thymus has a central role in immunity. According to a new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers, a hormone that extends lifespan in mice by 40%, is produced by specialized cells in the thymus gland. The team also found that increasing the levels of this hormone FGF21 protects against the loss of immune function that comes with age.
Liver – The liver helps to maintain normal immune activity.
From a Chinese Medicine perspective, the liver is responsible for part of the functions of the endocrine, digestive, circulatory and immune systems. The liver promotes flowing and spreading of Qi and blood through the entire body. And the Liver is also responsible for emotional harmony. TCM believes that emotional activity is an outer manifestation of the physiological status of the internal organ system, which is considered the major internal cause for diseases (regarded as endogenous evils in extreme conditions). When the liver keeps everything flowing smoothly, a regulated internal environment is created, keeping diseases out. In Chinese Medicine anger is the emotion associated with the Liver, although all emotions disrupt the Liver’s ability to do its job, to maintain a smooth flow of Qi in the body. The Qi is said to move the blood. So if you have Liver Qi stagnation, you will eventually wind up with Blood stagnation.
“Studies show a high level of correlation between immune function and the nervous system. Chronic stress and negative mood states such as grief or depression can reduce our ability to fight off an everyday cold or flu virus.”
Spleen – The spleen filters the blood, to remove bacteria, viruses, and foreign matter. In addition, the spleen contain the body’s own immune cells such as B cells, T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and red blood cells. When an immune response takes place in the spleen, B cells become activated and produce antibodies. In TCM the Spleen helps to determine the abundance and depletion of healthy energy, the body’s protection against disease, known as Wei Qi. The spleen is a brownish fist-sized organ located in the upper left side of the abdomen, between the stomach, pancreas and left kidney. Essentially, the spleen is the largest lymph node in the body. One of its tasks is to remove harmful bacteria and viruses in the blood stream. Its other major task is removing or storing certain blood cells.
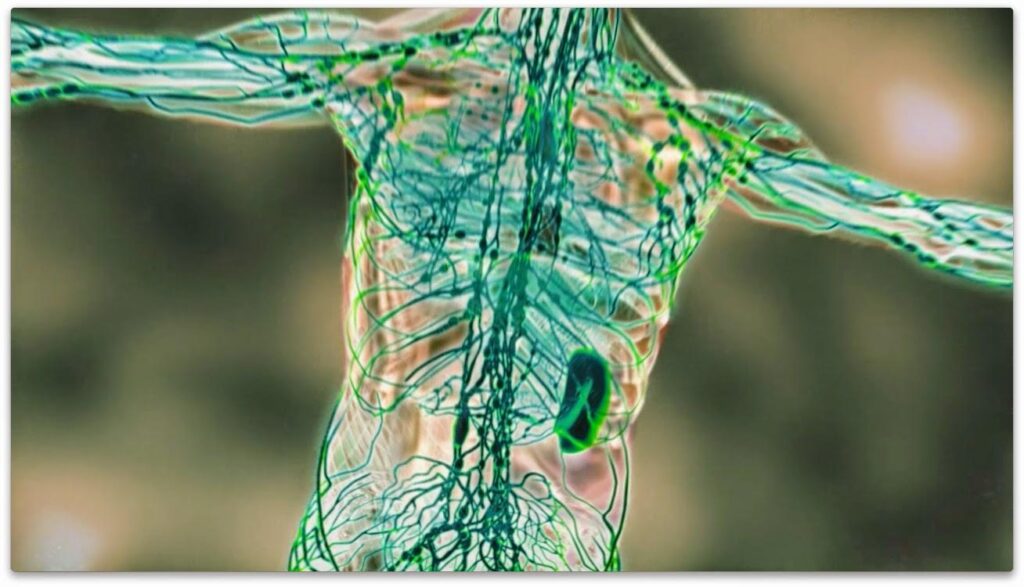
The lymphatic system. The spleen is your largest lymph node, located under the right ribs.
Lymphatic System – Clears toxins and parallels the blood circulation system. Different types of immune blood cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and plasma cells, circulate through the blood stream and the lymph channels. The lymph nodes constantly clean and drain fluids and toxins from all body tissues.
Kidneys – The kidneys are the foundation of Immunity in Chinese Medicine.
TCM views the kidneys as the “congenital foundation of life”, the root of healthy energy. The stored kidney essence is called Jing, and is the material basis for the body’s yin and yang forces, all 20 meridians, and protective Wei Qi. The kidneys play an important role in protecting the internal equilibrium. A strong kidney essence (Jing) promotes vitality and protective Wei Qi, strengthening the body’s resistance. In TCM the kidneys regulate the urinary system, reproductive system, blood, and nervous systems. Kidneys work closely with the endocrine system to regulate immune function.
Intestines – The inner layer of the intestines has critical immune functions.
Certain specialized cells absorb nutrients from digested food, while others form a barrier that secretes mucus and prevents microbes from entering cells. Still others specialized cells alert the immune system when a foreign pathogen is present. This inner layer of the intestines, called the epithelium, is coated with many tiny indentations known as crypts. At the bottom of each crypt is a small pool of epithelial stem cells, which constantly replenish the specialized cells of the intestinal epithelium, which only live for about five days. These stem cells can become any type of intestinal epithelial cell, however they do not have the multi-purpose diversity of embryonic stem cells, which can become any cell type in the body.
GALT – The Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT) is the gastrointestinal tract’s immune system, and works to protect the body from invasion by pathogens. The GALT is a type of mucous lymph tissue that stores immune cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, that attacks and defend against pathogens
Appendix – Recent research shows it is a “safe house” for the beneficial bacteria living in the human gut.
The appendix is a slender two- to four-inch pouch located near the juncture of the large and small intestines. Long denigrated as useless, the appendix now seems to exist for a very good reason. Researchers at Duke University Medical Center postulate that the beneficial bacteria stored in the appendix that aid digestion can ride out a bout of diarrhea that completely evacuates the intestines. These beneficial bacteria can then re-emerge after the storm to repopulate the gut. Their publication appears online in the Journal of Theoretical Biology. William Parker, PhD, and R. Randal Bollinger, MD, PhD, Duke professor emeritus in general surgery. The gut is populated with different microbes that help the digestive system break down the foods we eat. In return, the gut provides nourishment and safety to the bacteria. Parker now believes that the immune system cells found in the appendix are there to protect, rather than harm, the good bacteria.
What are the Specialized Cells of the Immune system?
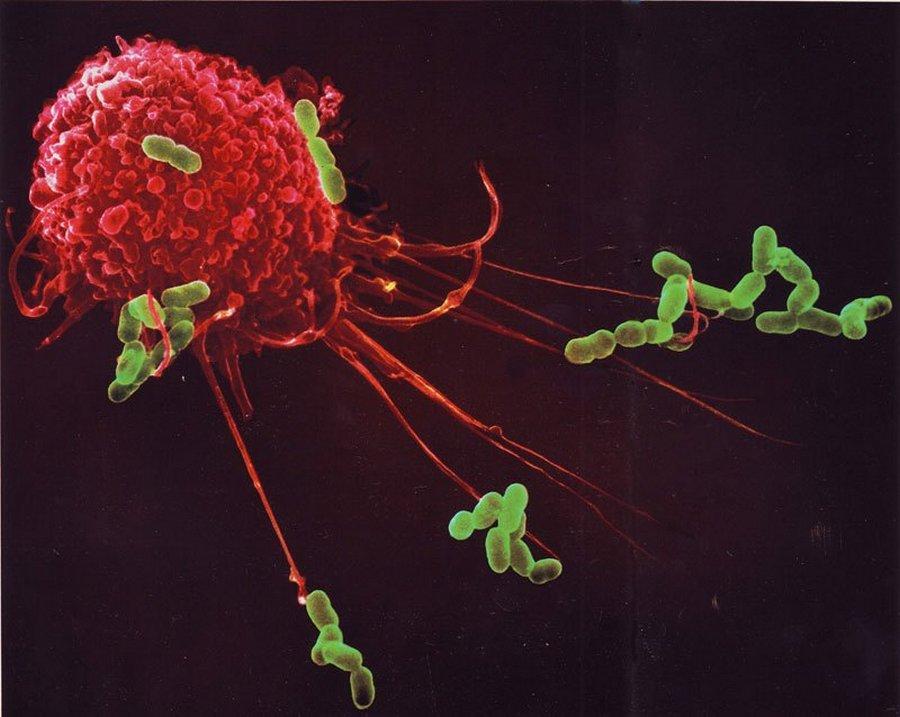
Human cells are mostly created in the bone marrow, and travel in the blood. They have specific purposes, such as Dendritic cells, which roam about the body looking for invaders. Macrophage literally means “big eater”. These cells extend “pseudopods”, or little feet to engulf and clear infections by eating bacteria, infected cells, and dead debris. Neutrophils, or white blood cells, are professional microbe-eaters that act like vacuum cleaners to consume microbe invaders. B cells and T cells are adaptive, in that they can shuffle their DNA to create new proteins that can detect new microbes, and create specific antibodies, for example to wipe out swine flu virus never seen before.
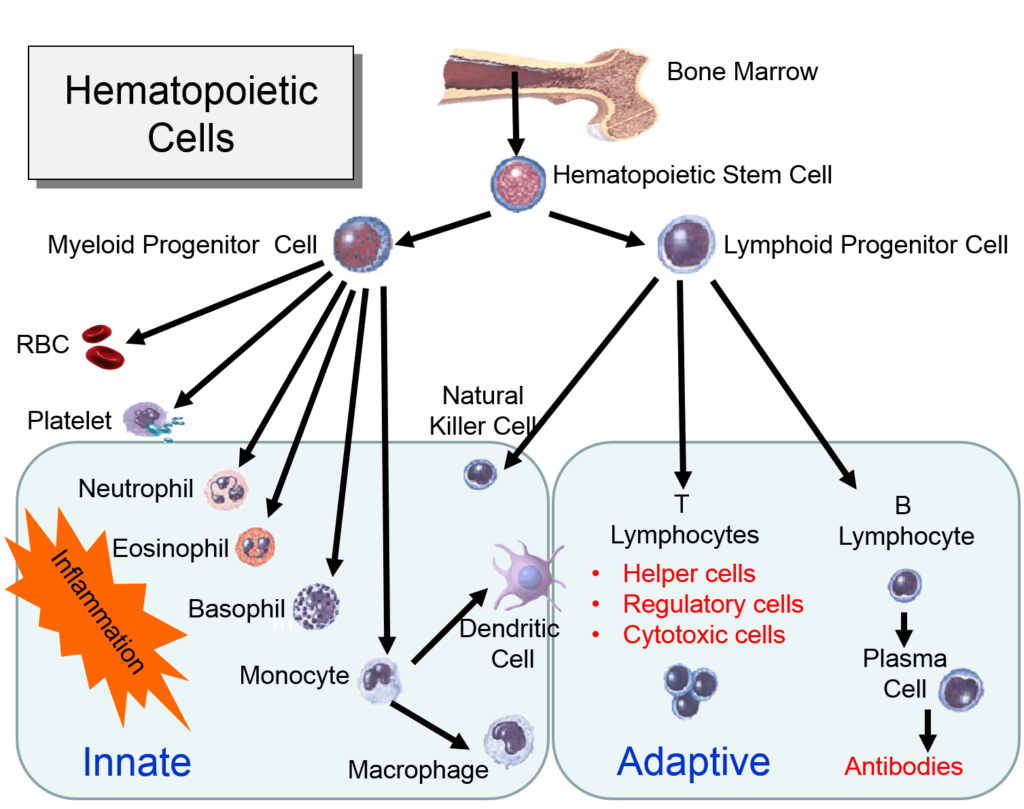
These specialized Blood Cells in the Immune System Originate in the Bone Marrow
The human body contains approximately ten to one hundred times as many bacterial cells as human cells. Known as commensal bacteria, they exist in a mutually beneficial, symbiotic relationship with their human hosts, helping with a diverse range of functions that are only beginning to be understood. While a majority of previous studies have focused on how bacteria shape and protect the immune system within the intestines, it is becoming clear that other sites of the body also benefit immensely from “good” bacteria.
First step in phagocytosis, or “cell eating” a macrophage extends several pseudopods from its single-celled form to embrace a number of E-coli bacteria.
History of the Immune System in the West
Early views of the immune system were influenced by terrible plagues, which wiped out millions of people in Europe. One enormous breakthrough in 1620 was the first multi-lens microscope in the Netherlands. Soon therafter in 1676, Dutch Van Leeuwenhoek discovered “protozoa”, single-celled organisms and called them “animalcules”. A few hundred years later in 1857, Louis Pasteur coined the “germ theory” with the discovery that fermentation and spoiled food were caused by microbes. This seems obvious to us now, however prior to Pasteur’s discovery of “germs”, people believed that only an act of God could bring living things from non-living things – a theory sometimes called “spontaneous generation”. Soon the new microscopes allowed us to differentiate bacteria from viruses, fungi, and parasites. Physicians learned that they could reduce deaths in childbirth by simply washing their hands. There arose a tendency to demonize all microbes as “germs” responsible for disease. Even now, we are offered anti-bacterial soaps, sani-wipes, and powerful antibiotics that kill all bacteria in order to get rid of a few pathogens. Unfortunately the Bad-germ theory represents a limited understanding of our symbiotic relationship with microbes.
How Does Ancient Chinese Medicine View the Immune System?
According to Chinese Medicine, fortifying the immune system relates to the Water Element, and cultivating the Jing, or the essential original energy held in the Kidneys. Strong Qi represents a delicate energy balance between the Kidneys, Lungs, Spleen, and Liver.
Chinese medicine focuses on cultivating our innate healing energies in a holistic way without focusing on a particular organ. TCM holds that the body has its own defense system that relies on the Zheng Qi, or Vital Energy. Chapter 72 of the oldest medical book, the Huangdi Neijing written 4,500 years ago, states: “When healthy energy is well stored inside the body, no evils can cause interference.” Chapter 33 states: “Whenever the evils are gathered inside, a deficiency of healthy energy must be present.” These statements imply that Zheng Qi, or Vital energy is the body’s natural resistance against disease, and disease is the result of the disharmonious healthy energy within the body.
The Chinese practiced the first known vaccines in the fifteenth century. They used a method of “nasal insufflation by blowing powdered smallpox material, usually scabs, up the nostrils through a silver tube. This was the first vaccination for variola, smallpox.
Paradigm-Breaking Research Reveals a New View of the Immune System
New super-high-powered microscopes have recently opened up a whole new world of microbes we never dreamed possible. Like Dr. Seuss’s story, “Horton Hears a Who”, we’re discovering that the vast majority of microbes are like a whole new civilization of “good guys”, working hard to make us healthy. New research shows the good microbes have specialized roles to protect our health. For example in the gut each microbe has an important task: Some of them create digestive enzymes to break food into molecular nutrients we can absorb. Some produce vitamins that we aren’t able to make ourselves. Other microbes defend us from pathogenic microbes that don’t belong in the body– the “bad guys”. Surprisingly we’re learning that most of the “good” microbes have been with us for millenniums, passed on from mothers to babies. The few pathogenic microbes are almost always present in the body, but kept under control by our immune system. These pathogens just wait patiently for an opportunity to proliferate, when the immune system weakens.
For example, new research shows that:
Microbiota – The trillions of bacteria that co-exist in the body, regulate the ability of lung dendritic cells to generate immune responses, according to a study by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, published online in the Journal of Experimental Medicine. “Our findings demonstrate a clear role of bacteria in modulating immune function in the lungs, which were long considered ‘sterile’ sites,” said Saurabh Mehandru, MD, senior author of the paper and Assistant Professor of Medicine in Gastroenterology. “This provides the basis to study other aspects of lung immune function that may be affected by microbial communities, and may also help with improving nasal vaccines used to protect against infections of the lung and elsewhere in the body.”
A team led by scientists from the Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and the University of Pittsburgh has shown how one set of specialized cells survives under stress by manipulating the behavior of key immune system cells. The new study, published in the journal Nature Communications, involved mesenchymal stem cells which live in bone marrow and can differentiate into several different cell types used in bone and connective tissue — and macrophages — immune cells that usually respond to infectious agents or damaged cells by engulfing and devouring them. “This is the first time anyone has shown how mesenchymal stem cells provide for their own survival by recruiting and then suppressing normal macrophage activity,”
Research in the UCR School of Medicine laboratory of David Lo found that certain cells of the epithelium layer of the intestines have an important role in immune surveillance – creating an electrostatic repulsion field to microbial invasion. “This is a whole new way of looking at immune surveillance in the epithelium of the human gut and airway,” said Lo, a distinguished professor in the medical school’s Division of Biomedical Sciences. “If we can take advantage of this electrostatic repulsion, it could improve the diagnosis and treatment of certain bacterial infections.” Lo’s laboratory has for more than a dozen years studied immune responses in the gut and airways, focusing particularly on cells which function as an early warning in the immune system. “We study the role of certain epithelial cells in the immune system. By understanding how the immune system is able to capture and carry viruses and bacteria across this barrier to trigger a protective immune, we may be able to design better synthetic vaccines, including needle-free vaccines,” Lo said.
Research by the Human Genome Project has ushered in a whole new paradigm and sympathetic understanding of the role of humans and microbes in life. In fact, the human body is a super-organism, or complex ecosystem of living cells, coexisting symbiotically with 100 trillion bacteria and other microbes. The vast majority of microbes reside in our skin, oral, nasal passages, and in the gut and reproductive systems are essential for our health, providing key functions that our body requires. In a mutually beneficial relationship, we provide them with a nice warm home, and they provide essential services for healthy digestion, brain function, and immune defense. Out of those 100 trillion bacteria, covering about 10,000 different species, there are only 50 – 100 strains that are known to be pathogens, that is, harmful to human life. There are so many helpful bacteria in the body that they may outnumber our actual human cells by a factor of 10 to 1, more likely 100 to one.
Research at the Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research indicates that the germinal centers in the body’s lymph nodes work as a fitness boot camp in which B cells evolve to produce antibodies of increasingly higher affinity to an invading pathogen. This new finding overturns a previously held notion that only a narrow range of B cells can survive this training and go on to secrete high-affinity antibodies. This revised understanding may aid development of effective vaccines against HIV, influenza, and other viruses that mutate rapidly.
Changes in the Global Micro-biome Bring Challenges to the Immune System
In the past 100 years, new types of stressors have arisen in our society that have a profound effect on the immune system. New microbes, GMO foods, increasing neurological stress, sensory overload, chemical toxins, lack of sleep, low nutrient foods, sedentary lifestyle, antibiotics, vaccines, global microbes, and increasing more opportunities to share microbes faster.
What was once a local, containable micro-biome in our hometown, has now become a global network of microbes. It’s like a worldwide bug fest! We often try to kill the bugs with anti-bacterial soaps and sani-wipes, pesticides, yard treatments, and chemical industrial agriculture. Yet it seems to hardly affect the bad microbes. Maybe all this is merely killing the good microbes that we need. And in the process, we’re also poisoning ourselves. GMO foods are very damaging on the gut micro-biome. Auto-immune diseases are now in epidemic proportions. All of it can be traced back to weak immunity.
“Recent changes in the global micro-biome have disturbed our delicate body eco-system, precipitating most of the major health issues we face today.”
 Potent plant antioxidants called Polyphenols in Green Tea are said to give it immune-boosting effects. One study suggested that Green Tea contains natural phytochemicals called catechins that may kill influenza viruses.
Potent plant antioxidants called Polyphenols in Green Tea are said to give it immune-boosting effects. One study suggested that Green Tea contains natural phytochemicals called catechins that may kill influenza viruses.
What to Do Now?
When we are ill, we go to the doctor, who is supposed to be our best resource, and we come away with pharmaceuticals that often suppress our true condition, or may have dangerous side effects. We look outside ourselves for pills, herbs, antibiotics, and supplements to restore our health. However after all is said and done, it is our simple daily lifestyle habits that either build or damage our immune system. This puts each of us squarely responsible for our health. Each person has a unique health journey that encompasses the destiny of our body, mind, and spirit as a whole. Read the top lifestyle habits to build your immune system in the first paragraph of this article. I wonder if the new idea of co-existing with the microbes holds some promise for health. Life will challenge us, and it’s not always simple. What an exciting journey it is!
Resources:
Body Ecology, a Course by Dr. John Veltheim and Laura Stuve, Ph.D. 2014, IBA, International BodyTalk Association, https://www.bodytalksystem.com
NIH – National Human Genome Research Institute, The Human Genome Project https://www.genome.gov/10001772
Drawing the Map of Life: Inside the Human Genome Project, by Victor K. McElheny
Science Daily: New study reveals how specialized cells help each other survive during times of stress https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/11/151103090537.htm
Science Daily: The immune system as specialized cells and organs that protect an organism from outside biological influences. https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/immune_system.htm
Can Your Immune System Still Defend You As You Age? https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/publication/biology-aging/immune-system-can-your-immune-system-still-defend-you-you-age
Yale News: Life-extending hormone bolsters the body’s immune function http://news.yale.edu/2016/01/11/life-extending-hormone-bolsters-body-s-immune-function
Shields Up! Research Reveals New, Protective Role for Specialized Cells in Intestinal and Respiratory Systems https://ucrtoday.ucr.edu/23661
Science Daily: B-cell diversity in immune system’s germinal centers may hold key to broad-spectrum vaccines https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/02/160218145137.htm
Cornell Medical School: Weill Cornell Investigators Discover a New Pathway that Prevents Chronic Inflammation in the Gut, INVESTIGATORS SHOW HOW IMMUNE CELLS ARE “EDUCATED” NOT TO ATTACK BENEFICIAL BACTERIA http://weill.cornell.edu/news/pr/2015/04/weill-cornell-investigators-discover-a-new-pathway-that-prevents-chronic-inflammation-in-the-gut.html
St. Jude’s Hospital: Discovery reveals how protective immune cells protect themselves https://www.stjude.org/media-resources/news-releases/2016-medicine-science-news/discovery-reveals-how-protective-immune-cells-protect-themselves.html
Rutgers Medical School: Paracrine effects of haematopoietic cells on human mesenchymal stem cells. http://njms.rutgers.edu/departments/medicine/divisions/stemcell/breakthroughs.cfm
Harvard Researchers Find Genetic Key to T Cell Differentiation http://news.harvard.edu/gazette/1996/07.11/HarvardResearch.html
Mt. Sinai Hospital: Commensal Bacteria Found to Regulate Immune Cells in Lungs to Produce Proteins Critical for Host Defense https://www.mountsinai.org/about-us/newsroom/press-releases/commensal-bacteria-found-to-regulate-immune-cells-in-lungs-to-produce-proteins-critical-for-host-defense
Study Explores How immune Cells Work Together in Inflammation http://lupusnewstoday.com/2015/09/16/study-explores-immune-cells-work-together-inflammation/
PRNewsWire: Discovery reveals how protective immune cells protect themselves http://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/discovery-reveals-how-protective-immune-cells-protect-themselves-300207960.html
Bone marrow and the control of immunity http://www.nature.com/cmi/journal/v9/n1/full/cmi201147a.html
Duke Medicine: Appendix Isn’t Useless at All: It’s a Safe House for Bacteria http://corporate.dukemedicine.org/news_and_publications/news_office/news/10151
Traditional Chinese Medicine Theory and Immunity http://www.shen-nong.com/eng/principles/tcmtheoryimmune.html
The spleen and its role in immune function
http://www.laparoscopic.md/digestion/spleen